Curriculum
ACADEMICS / CURRICULUM / COMPETENCES
ACADEMICS / CURRICULUM / MAJOR
ACADEMICS / CURRICULUM / COURSES
ACADEMICS / CURRICULUM / PRO-STEP
Competences
One of the educational programs of Universitas Multimedia Nusantara Faculty of Art & Design is an Architecture Study Program with a Bachelor of Architecture degree (S.Ars.)
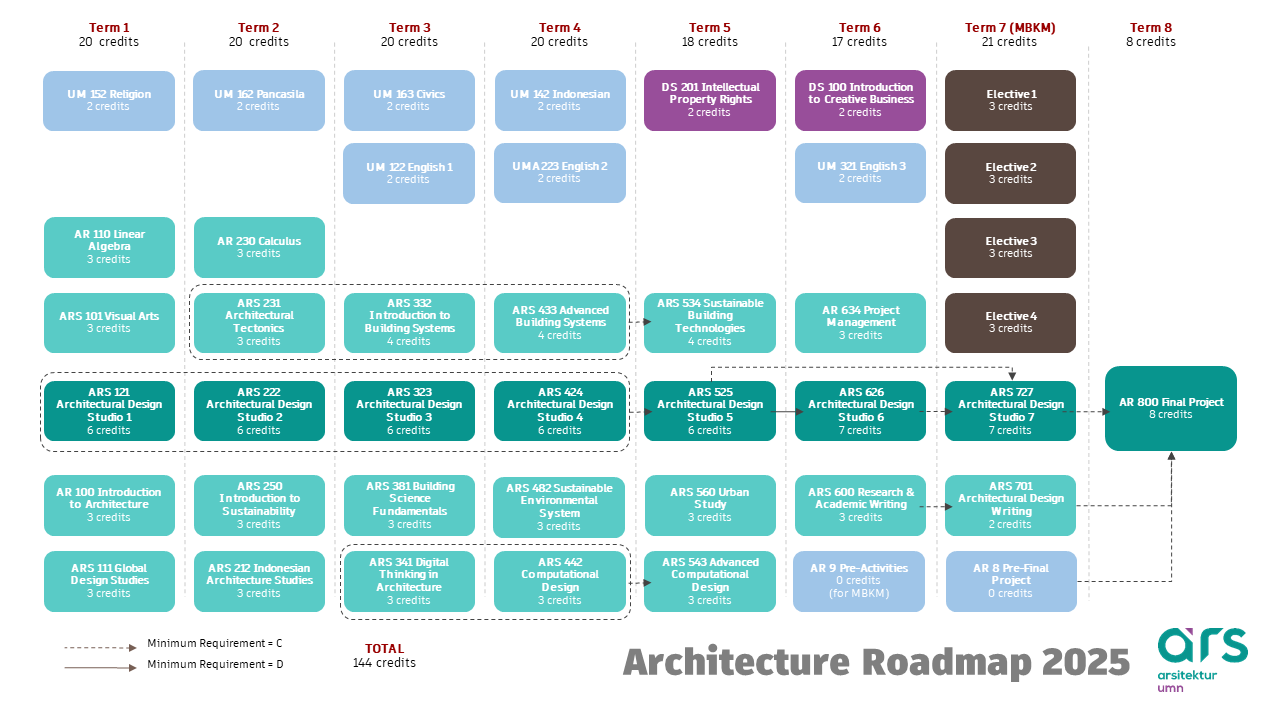
The Architecture Study Program specializes in Sustainable Architecture. The minimum study load for architecture undergraduate is 144 credit units (SKS) for 8 semesters or 4 years. We also offer Profession Program (PPAR).
Architecture Competences
Able to apply logical, critical, systematic, and innovative thinking in developing or implementing science and technology according to their field of expertise. Able to study the implications of development, science, technology, or art according to their expertise based on scientific principles, procedures, and ethics to produce solutions, ideas, designs, criticisms, and compile scientific descriptions of the results of their studies in the form of thesis reports and final assignments. Able to make appropriate decisions in the context of solving problems in their area of expertise, based on data information analysis. Able to manage to learn independently and develop and maintain a network with colleagues and peers both inside and outside the institution.
Able to develop architectural design concepts that integrate the results of studies of behavioral, environmental, technical, and values-related aspects of architecture through an ICT-based design process. Able to design architecture independently with an ICT-based design approach, and produce creative architectural works, to solve building environmental problems and improve the quality of a sustainable building environment. Using manual and digital techniques, able to communicate thoughts and design results in the form of graphics, writing, and communicative models. Able to present several alternative solutions for sustainable environmental design and make choice decisions based on architectural and scientific considerations supported by the use of ICT. Able to take advantage of the ability to design to assist in supervising and implementing environmental and building development.
Mastering the theoretical concepts of architecture, architectural design, aesthetics, structural systems, construction, and building utilities. Learning the principles of building and environmental science as a supporter of sustainable architectural design. Understanding the principles of ICT and multimedia that support the architectural design process
Honed Aspects
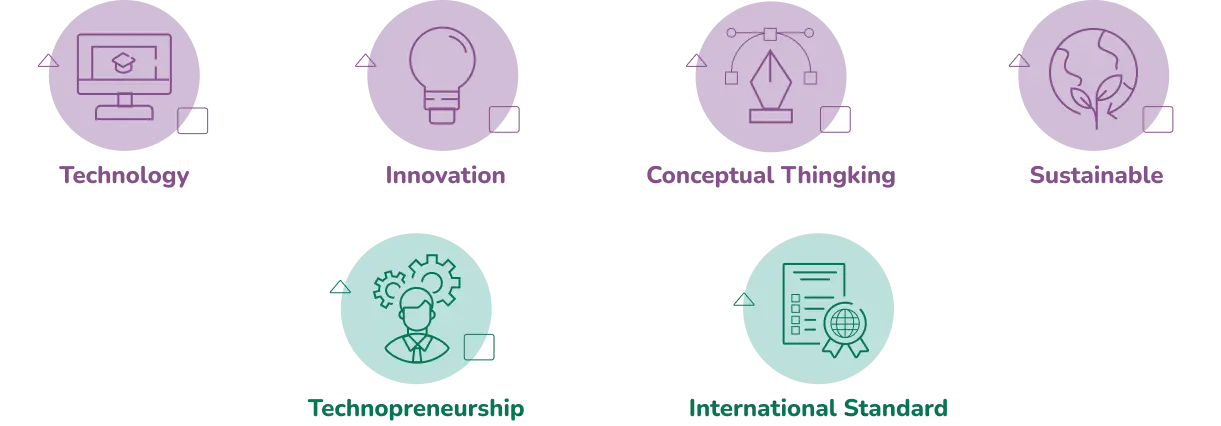
Expected Learning Outcomes (ELO) of ARSI-SP UMN are a combination of all leading aspects and learning from technology, sustainability, and innovation to compete in global industry with conceptual thinking, and technopreneurship.
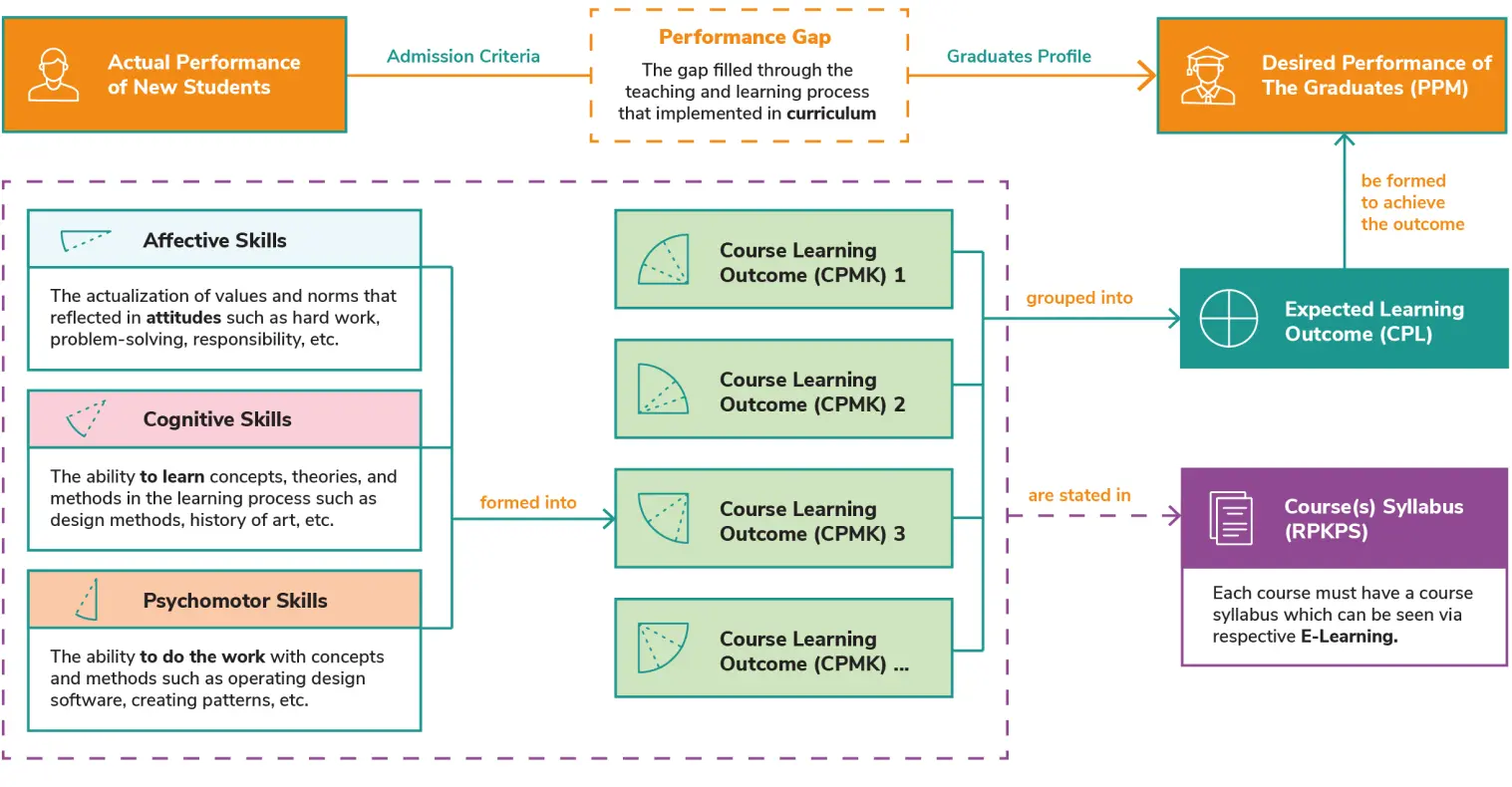
Outcome-Based Education
Outcome-Based Education (OBE) is an approach that emphasizes the sustainability of the learning process where at the end of the study, each student must be able to achieve the goals set by the Architecture Study Program.
Competences
Expected Learning Outcome
| Code | ELO Formula |
| ELO 1 | Ability to reconcile divergent factors in architecture theory through research & design thinking to make an integration program and design solution. |
| ELO 2 | Ability to understand the basic principles of 2D and 3D forms and design, exploration of design, architectural composition and to apply such principles to generate creative forms and spaces. |
| ELO 3 | Understanding of design procedures and processes through knowledge and experimentation of design theory and methods. |
| ELO 4 | Ability to demonstrate knowledge of historical and cultural precedents in architecture, both globally and locally, with a nuanced comprehension of the philosophy and principles underlying Indonesian architecture, fostering awareness of heritage preservation in architectural practice towards sustainability. |
| ELO 5 | Ability to promote interdisciplinary collaboration among architecture, science, technology, and fine arts, while developing noble character as they innovate and address complex challenges in the built environment. |
| ELO 6 | Ability to develop architectural projects that adhere to Sustainable Development Goals and consider environmental and societal impacts to promote ecological, social, and economic sustainability. |
| ELO 7 | Understanding urban theory and considering regional, social, cultural, economic, and policy aspects of urban/city planning and their mutual relationships to apply in architectural design. |
| ELO 8 | Understanding of technical knowledge for structure, materials, and construction, the process of technical design and the integration as a functionally effective whole, service systems, and impact of geotechnical and climate on urban and architectural design and construction. |
| ELO 9 | Ability to effectively express and communicate architectural ideas verbally and nonverbally, utilizing BIM and other multimedia of emerging ICT development while employing digital thinking in design realization process to convey concepts comprehensively and creatively. |
| ELO 10 | Understanding of the fundamental workings of the construction and development industries, professional ethics and codes for architects, the roles of architects, business principles, project management, and diverse forms of procurement of architectural services. |
Competences
Lifelong Learning
| No. | Key Competence Lifelong Learning | ELO1 | ELO2 | ELO3 | ELO4 | ELO5 | ELO6 | ELO7 | ELO8 |
| 1 | Communication in the mother tongue | v | v | v | |||||
| 2 | Communication in foreign language | v | v | v | |||||
| 3 | Mathematical competence and basic competences in science and technology | v | v | v | |||||
| 4 | Digital competence | v | v | v | |||||
| 5 | Learning to learn | v | v | v | |||||
| 6 | Social and civic competences | v | v | v | |||||
| 7 | Sense of initiative and entrepreneurship | v | v | ||||||
| 8 | Cultural awareness and expression | v | v | v |
Industries’ Needs Related to ELO
| Job Title/ Profession | Job Description | ELO | Concentration Courses | |||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |||
| Graphic Designer | Design a visualization of concepts and layout | v | v | v | v | v | v | Visual Brand Design | ||
| Art Director | Design and be responsible for the visual concept of visual advertising | v | v | v | v | v | v | |||
| Creative Director | Design and be responsible for creative and media strategies | v | v | v | v | v | v | v | v | |
| Copywriter | Design persuasive words as the main support in advertising | v | v | v | ||||||
| Junior Designer | Design a visualization of translating brand concepts | v | v | v | v | |||||
| Senior Designer | Design and be responsible for creative concepts and brand visuals | v | v | v | v | v | ||||
| Technopreneur | Design be responsible and run the development of a creative industry-based business | v | v | v | v | v | v | v | v | |
| Asset Designer | Designing visual media assets both digital and non-digital interactive | v | v | v | v | v | v | Interaction Design | ||
| Junior Designer | Design visualization of interactive concept translation | v | v | v | v | |||||
| Senior Designer | Designing and being responsible for creative concepts and interactive media | v | v | v | v | v | v | |||
| User Experience (UX) Designer | Perform user tests on interactive media | v | v | v | v | v | v | v | ||
| Art Director | Designing and being responsible for the interactive concepts of the media | v | v | v | v | v | v | v | v | |
| Interaction Design | Design and be responsible for patterns and concepts of interaction on interactive media | v | v | v | v | v | v | v | ||
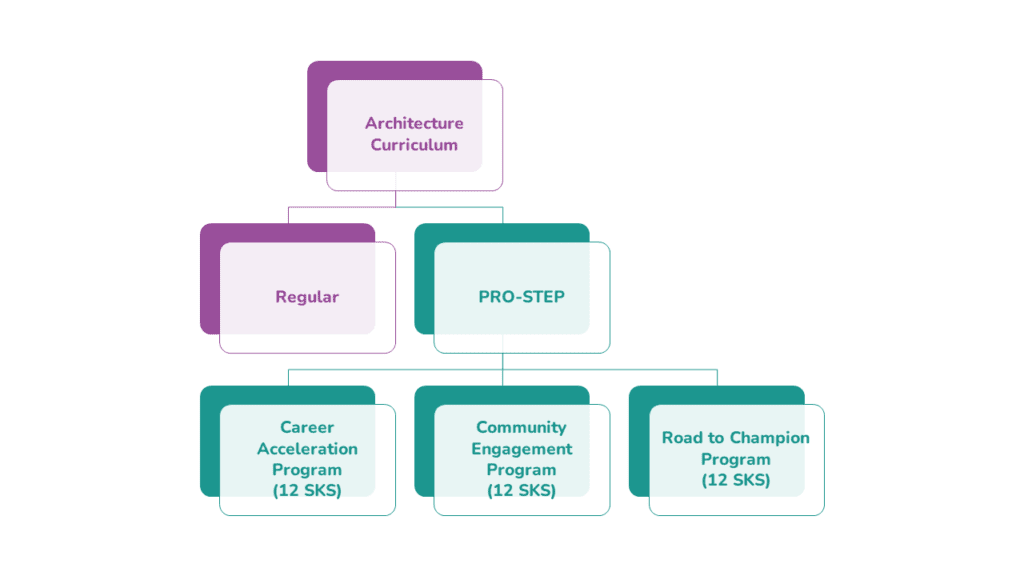
PO-STEP
The Professional Skill Enhancement Program (PRO-STEP) program grants undergraduate architecture students the freedom to take courses outside the architecture department (interdepartmental) or architectural courses at partner universities. Selected PRO-STEP activities that students can participate in, as follows:
- Carrer Acceleration Program
- Community Engagement Program
- Road to Champion Program
Requirements
The following is a guide to using the UMN Kampus Merdeka system at merdeka.umn.ac.id.